The threaded rod, seemingly an ordinary fastener, serves as a critical link in connecting the world’s structures. Meigesi’s threaded rods are renowned for their strength, versatility, and customizability—making them the ideal solution for structural reinforcement and support across construction, electromechanical systems, furniture manufacturing, and industrial equipment. They deliver maximum efficiency and reliability at minimal cost.
Threaded rod, also known as all-thread rod, is a metal straight bar featuring continuous or partial threading along its length, widely used across industrial and engineering fields. Characterized by high tensile strength and excellent shear resistance, threaded rods can be cut to any required length, offering exceptional flexibility in application. Commonly used for load-bearing connections and structural reinforcement, they provide reliable support in construction, electrical installations, piping systems, manufacturing, and more. This article provides a comprehensive overview of threaded rods, covering their definition, technical background, application areas, material specifications, installation methods, and the competitive advantages of the Meigesi brand.
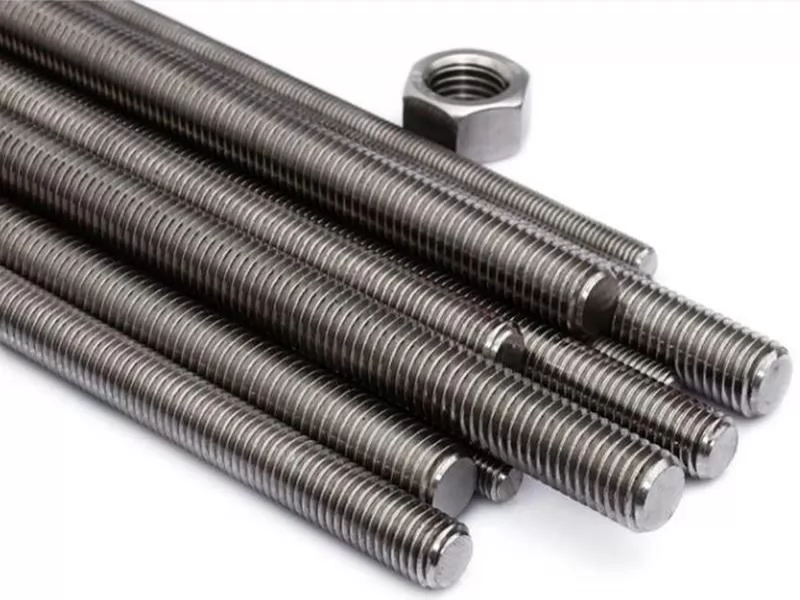

Threaded rod is a type of metal fastener featuring continuous or partial threading along its length, designed for structural connection and support. Unlike standard bolts, threaded rods do not have a formed head, allowing nuts to be positioned and secured at any point along the rod—making them ideal for applications requiring adjustable length. Commonly referred to as all-thread rod or stud, these products are manufactured to international standards, such as DIN 975 or DIN 976 for metric specifications, and ASTM A193/A307 for imperial specifications. Standard stock lengths are typically 1 meter, but rods can be cut to custom lengths as required using appropriate cutting tools. Typical applications include equipment positioning adjustment, structural bracing, and ceiling installations, where their simple yet functional design offers practical solutions. To meet varying strength requirements, threaded rods are commonly produced from low carbon steel, high-strength carbon steel (grades 4.8, 8.8), stainless steel (304, 316), or brass. Surface treatments such as black oxide coating or zinc plating are applied to enhance corrosion resistance.
Thanks to its versatility and high strength, threaded rod is widely used across various industries. Typical application scenarios include:
Construction Engineering:
Threaded rods are essential for concrete anchoring and steel structure connections. They can serve as foundation bolts, formwork supports, or frame reinforcement components. For example, they can be embedded in concrete as anchor bolts or used to suspend heavy equipment and pipelines. Their high load-bearing capacity and adjustable length make them ideal for creating stable and reliable support systems in construction.
Mechanical and Electrical Installation (M&E):
In the installation and maintenance of mechanical and electrical equipment, threaded rods are commonly used to suspend or secure air conditioning ducts, ventilation systems, and heavy machinery bases. Threaded rods can efficiently bear equipment weight and maintain proper positioning, while also allowing for easy and rapid installation.
Electrical Engineering:
In electrical wiring and distribution systems, threaded rods are used to support cable trays, lighting fixtures, and distribution panels. Combined with nuts and washers, they allow cable trays and electrical panels to be suspended from ceilings or beams securely, ensuring stable electrical installations with clean, organized cabling.
Pipe Support Systems:
In plumbing and HVAC applications, threaded rods act as structural supports for pipes, equipment, and valves. For instance, they are used to secure horizontal pipelines or vertically support risers, maintaining accurate alignment and slope. Thanks to their high corrosion resistance, threaded rods are also suitable for supporting piping systems in corrosive environments.
Furniture and Industrial Manufacturing:
In furniture making and equipment production, threaded rods are used to connect and reinforce structural components and serve as adjustable connectors. For example, furniture manufacturers often use threaded rods to build adjustable table legs or bookshelf brackets. In machinery manufacturing, they are commonly used for jigs, positioning systems, and tensioning devices, enhancing structural stability and flexibility.
These applications are only examples—threaded rods can be cut and spliced as needed, making them suitable for nearly any situation requiring strong connections or suspended support, including bridges, tunnels, power equipment, vehicle assembly, interior decoration, and more.

The material and specifications of the thread rod will directly affect its mechanical properties and applicable environment. Common materials include low carbon steel, high-strength carbon steel (such as 4.8, 8.8 grades), stainless steel (304, 316), brass and aluminum. The characteristics and applicable scenarios of different materials are as follows:
|
Material |
Characteristics |
Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
|
Carbon Steel (Grade 4.8) |
Moderate strength, cost-effective; typically zinc-plated for corrosion resistance. |
Indoor structural supports, assembly lines, general mechanical components; suitable for environments with low corrosion requirements. |
|
High-Strength Carbon Steel (Grade 8.8 and above) |
High strength and rigidity; generally black oxide or zinc-plated for protection; ideal for high-load structures. |
Heavy machinery, industrial equipment installation, bridge steel structures, and other load-bearing applications. |
|
Stainless Steel (304/316) |
Excellent corrosion and high-temperature resistance; superior mechanical properties; suitable for harsh environments. |
Chemical and petrochemical industries, marine platforms, food processing equipment, and other hygienic or corrosive environments. |
|
Brass |
Good electrical conductivity, excellent corrosion resistance, and an attractive appearance. |
Electrical fittings, decorative components, sanitary ware, and other applications requiring corrosion resistance or conductivity. |
|
Aluminum Alloy |
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant; lower strength compared to steel; typically used for light-load applications. |
Lightweight supports, electronic equipment mounting, aerospace structures, and other weight-sensitive applications. |
At the same time, the thread outer diameter and pitch of the thread rod are produced according to standard sizes. For example, common specifications M3~M30 (carbon steel, 304/316 and other materials) are in stock, and the length can reach more than 6 meters. Rods longer than 1 meter are mostly customized, and rods within 1 meter can be cut and supplied. For occasions with high corrosion protection requirements, the surface can also be hot-dip galvanized, ordinary galvanized or coated to improve weather resistance. Hot-dip galvanizing coating is a common treatment method for outdoor environments, which can significantly enhance the rust resistance of the thread rod.
The installation of the thread rod is simple and convenient, and can be flexibly applied according to specific needs. The usual steps are: first measure the required length according to the application, cut the thread rod to the appropriate size with a hacksaw or angle grinder, and trim the burrs at the cut; then insert the thread rod into the reserved hole or hang it on the bracket, and use nuts and washers to fix and tighten it. During installation, the reserved nuts at both ends or in the middle can be screwed in to adjust the preload force and installation height. For occasions where longer thread rods need to be connected, connecting nuts (butt nuts) can also be used to splice two sections of thread rods into a whole to extend the installation distance. During the entire installation process, a stable connection can be achieved by relying solely on the principle of threaded fastening, eliminating riveting or welding operations, and the operation is convenient and flexible.
As an industry-leading brand, Meigesi Fastener has earned customer trust through strict quality control and tailored service advantages:
1. Premium Quality Assurance:
Meigesi selects high-grade raw materials that comply with international standards and utilizes advanced manufacturing equipment along with comprehensive inspection procedures. Every threaded rod undergoes rigorous quality checks from incoming materials to finished products, ensuring precise dimensions and consistent performance that meet the highest standards.
2. Comprehensive Specifications & Customization:
With a full range of standard specifications kept in stock for rapid delivery, Meigesi also offers custom production services based on client drawings and specific requirements. This enables the precise manufacturing of threaded rods in special sizes, materials, and strength grades to suit diverse project needs.
3. Technical Support:
Backed by an experienced engineering team, Meigesi provides professional technical support including thread selection recommendations, structural installation guidance, and solutions to application challenges, ensuring optimal results for every project.
4. Complete Customer Service:
With responsive communication and timely delivery, Meigesi offers a comprehensive pre-sales and after-sales service system. Continuous follow-up ensures customer needs are met throughout the entire usage cycle of the product.
DIN 975 threaded rods are long rods with continuous threads running along their entire length, designed for tension joining and stabilizing purposes. Unlike screws or bolts, these rods do not have heads, making them highly versatile for various applications. Also referred to as all-thread rods (ATR), fully threaded rods, continuously threaded rods, or redi-rods, they are typically available in steel and stainless steel (A2 and A4) grades, with diameters ranging from M3 to M56.
B7 Galvanized Carbon Steel Threaded Rods are high-strength fasteners crafted from a medium-carbon steel alloy, specifically designed to withstand demanding conditions. This alloy is enriched with chromium and molybdenum, which enhance its resistance to wear and corrosion. The rods undergo a quenching and tempering process to achieve exceptional tensile strength and durability, with a minimum tensile strength of 125,000 psi and a yield strength of 105,000 psi.
B7 Black Threaded Rod is an alloy steel Threaded Rod used in high temperature and high pressure environments. Made of chromium-molybdenum alloy steel, this Threaded Rod is the preferred connection element for equipment subjected to extreme conditions. This Threaded Rod is corrosion-resistant, high temperature-resistant, and tough, making it more suitable for scenarios that require high-quality connections.
If you want to know more details about thread rod, please ask us.